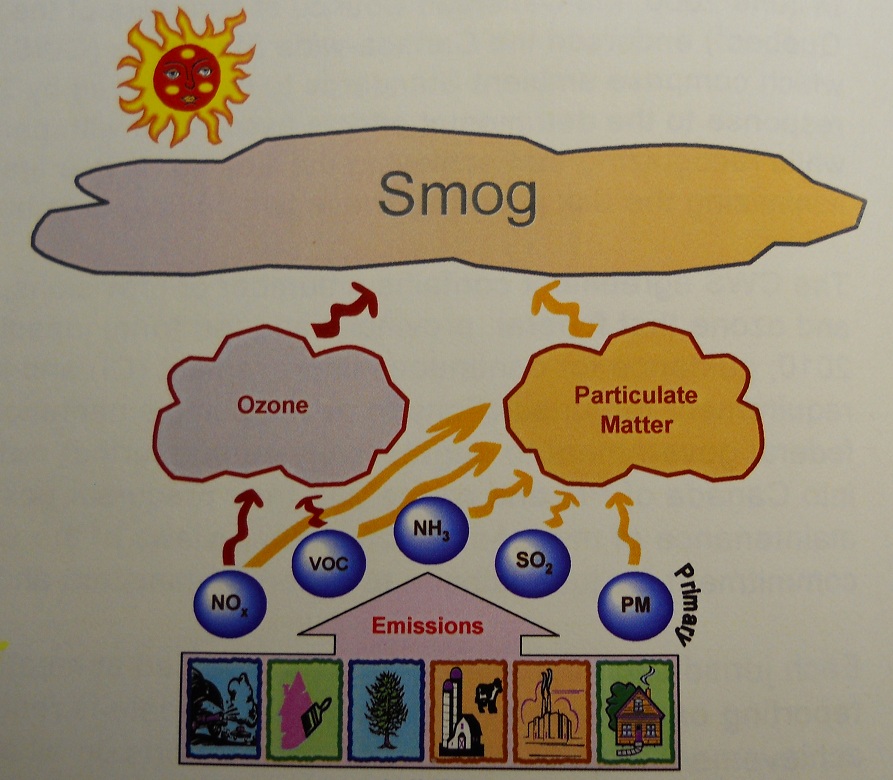
SMOG AND ITS EFFECTS
Smog is one of the most recognizable air quality problems in
Canada. It refers to a noxious mixture of air
pollutants which often gives the air a hazy appearance. The major components of smog in Canada are
ozone and particulate matter (PM) in the summer, and PM in winter. These pollutants have been linked to a number
of adverse effects on human health and the environment.
PM refers to microscopic solid and liquid particles that
remain suspended in the air. Particles
are what make the air look hazy on days with smog since they impair
visibility. Ozone is a colourless gas
that forms in the air. Smog-producing
pollutants include direct PM emissions and the gases sulphur dioxide (SO2),
nitrogen oxides (NOx), volatile organic compounds (VOC) and ammonia
(NH3).
In summer, large-scale smog episodes are typically
associated with slow-moving high pressure systems, which bring with them very
high temperatures, light winds and a times stagnant conditions, both of which
allow the build-up of locally emitted pollutants. In the eastern part of Canada, southerly winds typically accompany
these episodes, bringing with them pollutants from the United States. In winter, large-scale smog episodes are
typically associated with high levels of PM, often brought about by a build-up
of locally emitted pollutants under stagnant air.
Smog is a concern in many urban centres across Canada,
and it can also be a concern in rural undeveloped areas, since emissions of
smog-producing pollutants can be transported by the prevailing airflows over
large distances and affect air quality in areas hundreds to thousands of
kilometres away from their sources.