Description
2
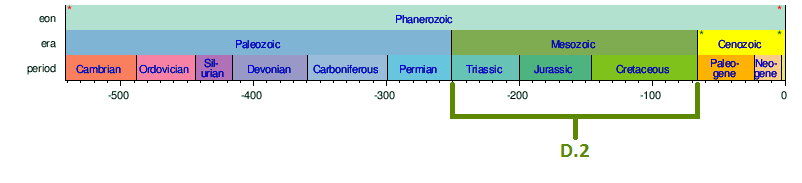
Description (D.2)
|
Supereon ------------- |
Eon Phanerozoic |
Era Mesozoic |
Period Cretaceous |
Epoch Late Early |
Age - Maastrichtian - Campanian - Santonian - Coniacian - Turonian - Cenomanian - Albian - Aptian - Barremian - Hauterivian - Valanginian - Berriasian |
Start, Ma ago 70.6 ± 0.6 83.5 ± 0.7 85.8 ± 0.7 89.3 ± 1.0 93.5 ± 0.8 99.6 ± 0.9 112.0 ± 1.0 125.0 ± 1.0 130.0 ± 1.5 136.4 ± 2.0 140.2 ± 3.0 145.5 ± 4.0 |
Major events
Flowering plants proliferate, along with new types of insects. More modern teleost fish begin to appear. Ammonites, belemnites, rudist bivalves, echinoids and sponges all common. Many new types of dinosaurs (e.g. Tyrannosaurs, Titanosaurs, duck bills, and horned dinosaurs) evolve on land, as do Eusuchia (modern crocodilians); and mosasaurs and modern sharks appear in the sea. Primitive birds gradually replace pterosaurs. Monotremes, marsupials and placental mammals appear. Break up of Gondwana. Beginning of Laramide and Sevier Orogenies of the Rocky Mountains. Atmospheric CO2 close to present-day levels.
Description (D.2)
|
Supereon ----------- |
Eon Phanerozoic |
Era Mesozoic |
Period Jurassic |
Epoch Late Middle Early |
Age - Tithonian - Kimmeridgian - Oxfordian - Callovian - Bathonian - Bajocian - Aalenian - Toarcian - Pliensbachian - Sinemurian - Hettangian |
Start, Ma ago - 150.8 ± 4.0 - 155.7 ± 4.0 - 161.2 ± 4.0 - 164.7 ± 4.0 - 167.7 ± 3.5 - 171.6 ± 3.0 - 175.6 ± 2.0 - 183.0 ± 1.5 - 189.6 ± 1.5 - 196.5 ± 1.0 - 199.6 ± 0.6 |
Major events
Gymnosperms
(especially conifers,
Bennettitales
and cycads) and ferns common. Many
types of dinosaurs,
such as sauropods,
carnosaurs,
and stegosaurs.
Mammals common but small. First birds and lizards. Ichthyosaurs and plesiosaurs
diverse. Bivalves,
Ammonites
and belemnites
abundant. Sea
urchins very common, along with crinoids,
starfish, sponges,
and terebratulid
and rhynchonellid
brachiopods.
Breakup of Pangaea
into Gondwana
and Laurasia.
Nevadan
orogeny in
Description (D.2)
|
Supereon ----------- |
Eon Phanerozoic |
Era Mesozoic |
Period Triassic |
Epoch Late Middle Early |
Age - Rhaetian - Norian - Carnian - Ladinian - Anisian - Olenekian - Induan |
Start, Ma ago - 203.6 ± 1.5 - 216.5 ± 2.0 - 228.0 ± 2.0 - 237.0 ± 2.0 - 245.0 ± 1.5 - 249.7 ± 1.5 - 251.0 ± 0.7 |
Major events
Archosaurs dominant on land as dinosaurs, in the oceans as Ichthyosaurs and nothosaurs, and in the air as pterosaurs. Cynodonts become smaller and more mammal-like, while first mammals and crocodilia appear. Dicroidium flora common on land. Many large aquatic temnospondyl amphibians. Ceratitic ammonoids extremely common. Modern corals and teleost fish appear, as do many modern insect clades. Andean Orogeny in South America. Cimmerian Orogeny in Asia. Rangitata Orogeny begins in New Zealand. Hunter-Bowen Orogeny in Northern Australia, Queensland and New South Wales ends, (c. 260–225 Ma)


